Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease: Protect Your Child From The Viral Rash
- Indian Health Bureau
- Sep 18, 2025
- 2 min read
A viral illness, Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD), is quickly spreading among children in Delhi and nearby Haryana, leading health experts and schools to issue urgent advisories. This infection, which mainly affects those under 10 years old, does not have any targeted treatment available, so doctors emphasize that only preventive steps and attentive care at home are effective in managing cases.
In response, Delhi’s Directorate of Education has released detailed guidelines for schools and parents, warning them to watch for symptoms like fever, rashes on the hands and feet, mouth blisters, sore throat, and irritability. The advisory also instructs families not to send children with these symptoms to school, to help curb further transmission.
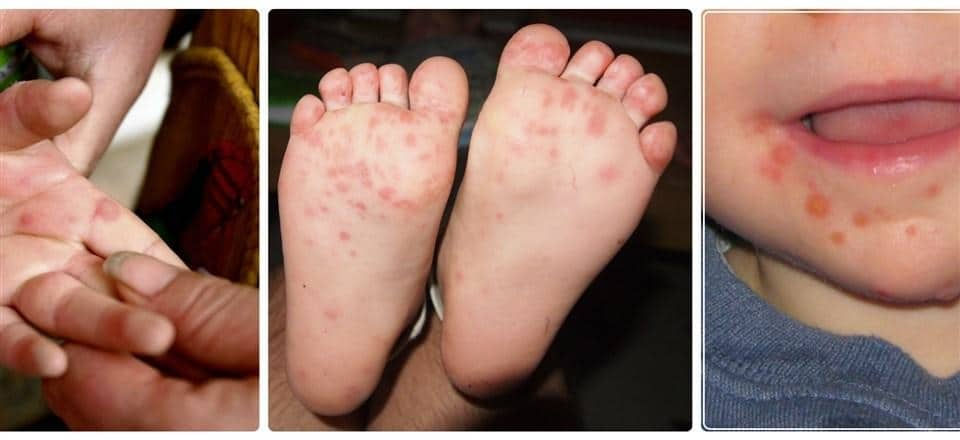
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a contagious viral infection primarily affecting young children, characterized by fever, mouth sores, and a rash on the hands, feet, and sometimes the buttocks and groin.
What Is HFMD?
HFMD is a mild but bothersome viral infection, most frequently seen in children under age five, though anyone can get it. It is most commonly caused by coxsackievirus A16 or enterovirus 71, both members of the Enterovirus genus.
How to Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
Fever, sore throat, reduced appetite, and a general sense of feeling unwell often come first.
Within a day or two, painful blisters or ulcers develop in the mouth—especially on the tongue, gums, and inside of cheeks.
A rash of red spots or blisters appears on the palms of hands, soles of feet, and sometimes on the buttocks, knees, or elbows.
Other signs to watch: irritability, drooling (from mouth pain), and wanting only cold drinks.
How HFMD Spreads
The virus travels fast! It spreads through direct contact with infected people’s saliva, mucus, stool, or blisters, as well as contaminated objects and surfaces.
The period when someone is most contagious is the first week of illness, even if symptoms are mild.
Treatment and Recovery
There’s no cure or specific medication for HFMD.
Treatment focuses on comfort—rest, plenty of fluids, and pain/fever reducers such as ibuprofen or paracetamol.
Antibiotics are not helpful, as HFMD is caused by a virus, not bacteria.
Most children recover fully within 7–10 days.
Prevention Tips
Regular handwashing with soap and water is the single most effective way to prevent spread.
Disinfect toys, surfaces, and common areas, especially in schools and daycare settings.
Keep ill children home until rashes and fevers subside, so outbreaks are less likely.
When to Contact a Doctor
Seek medical advice if a child refuses fluids, shows signs of dehydration, or symptoms worsen after a few days.
Rarely, HFMD can lead to complications like meningitis or encephalitis—watch for prolonged fever, confusion, stiff neck, or unusual drowsiness.
Although HFMD is typically mild, it can cause quite a discomfort for children and anxiety for parents. Good hygiene and a calm approach to symptom care help most families through it quickly and safely.
Share this guide to help friends and fellow parents keep kids healthy and HFMD-free




Comments